Yong Sheng Sports Goods Co., Ltd. - Neoprene Fabric Division
Professional Neoprene Fabric Manufacturers and OK Fabric Suppliers in China
Professional Neoprene Fabric Manufacturers and OK Fabric Suppliers in China
ECO Limestone Neoprene & Plant Based Rubber - Manufacturers and Suppliers
Neoprene was invented by DuPont in the United States in the 1930s. It is a synthetic rubber based on the polymerization of petroleum through chloroprene. It was originally used as an oil-resistant substitute for natural rubber. It was used in wetsuits in the 1950s. In the 1960s, Japan YAMAMOTO developed a neoprene based on limestone production, and several manufacturers in Taiwan developed similar products. After entering the 21st century, with the development of green environmental protection and renewable concepts, wetsuits made from natural rubber produced from renewable plants are gradually appearing on the market.
Based on petroleum-produced neoprene, the presence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds (PAHs) and other related harmful substances is inevitable and can only be minimized during the production process. Based on the production of neoprene in limestone, the content of related harmful substances can be kept at a low level due to the raw materials, and products that pass the Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 Class II test can be supplied. Natural plant rubber based on renewable plants (Guayule / Dandelion), we usually call it green rubber.
ECO Neoprene Sponge
Explain: "ECO Neoprene Sponge" By optimizing the process and special treatment in the production process, the purpose of reducing the content of related harmful substances is achieved. We can offer this type of product.
Advantages & Disadvantages: The price is relatively cheap, the supply is stable, and it is easy to obtain, but it cannot pass the high standard inspection requirements.
Limestone ECO Neoprene Sponge
Explain: "Limestone ECO Neoprene Sponge" is a synthetic rubber produced by the polymerization of acetylene gas produced by burning limestone. We can offer this type of product.
Advantages & Disadvantages: It has more microporous cells than petroleum-based neoprene. It has lighter weight, better elasticity, less harmful substances, but is expensive. As time goes by, the thickness will become thinner and brittle. Surface strength is low (Smooth Skin).
Guayule / Dandelion Plant-Based Rubber
Explain: Natural plant rubber based on American guayule or Russian dandelion, does not contain sensitizing antigen protein (latex allergy), and is used to replace traditional neoprene wetsuit. This is the leading product of Yulex® and we are not currently offering such products.
Advantages & Disadvantages: Green and environmentally friendly, the price is very expensive, limited by the planting area and growth rate, and the supply is limited.
Yong Sheng ECO-Neoprene Sponge Can Fulfill The Below International Standards:
| REACH | 151 substances in the Candidate List of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) for Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 concerning the REACH |
| RoHS | Restriction of Hazardous Substances - RoHS 2.0 Directive 2011/65/EU Annex II ; Recasting 2002/95/EC |
| Toxic Elements | Migration of Certain Elements - EN 71-3:1994+A1:2000+AC:2002 |
SGS Test Report (ECO-Neoprene Fabric):

SGS REACH Test

SGS RoHS Test

SGS Toxic Elements Test
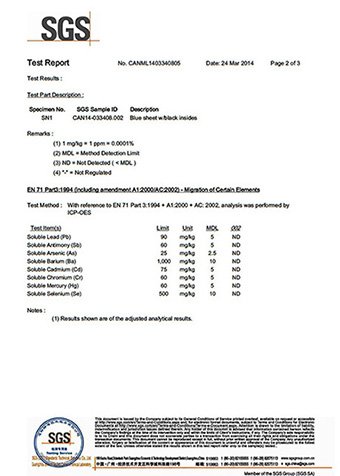
SGS Toxic Elements Test
Description of SGS Test Products:
ECO-Neoprene Sponge Laminated ECO-Fabric made of Nylon, Polyester, Lycra, Dyed and Finished.
Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 Class II Certificated ECO Limestone Neoprene Sponge:
| Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 Test Standard(Executed from April 1, 2018) | ||||
| Product Class | I | II | III | IV |
| Baby | In Direct Contact With Skin | With No Direct Contact With Skin | Decoration Material | |
| pH value | ||||
| 4.0 - 7.5 | 4.0 - 7.5 | 4.0 - 9.0 | 4.0 - 9.0 | |
| Formaldehyde, free and partially releasable [mg/kg] | ||||
| Law 112 | n.d. | < 75 | < 150 | < 300 |
| Extractable (heavy) metals [mg/kg] | ||||
| Sb (Antimony) | < 30.0 | < 30.0 | < 30.0 | |
| As (Arsenic) | < 0.2 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Pb (Lead) | < 0.2 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Cd (Cadmium) | < 0.1 | < 0.1 | < 0.1 | < 0.1 |
| Cr (Chromium) | < 1.0 | < 2.0 | < 2.0 | < 2.0 |
| Cr (VI) | < 0.5 | |||
| Co (Cobalt) | < 1.0 | < 4.0 | < 4.0 | < 4.0 |
| Cu (Copper) | < 25.0 | < 50.0 | < 50.0 | < 50.0 |
| Ni (Nickel) | < 1.0 | < 4.0 | < 4.0 | < 4.0 |
| Hg (Mercury) | < 0.02 | < 0.02 | < 0.02 | < 0.02 |
| Ba (Barium) | < 1000 | < 1000 | < 1000 | < 1000 |
| Se (Selenium) | < 100 | < 100 | < 100 | < 100 |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) [mg/kg] | ||||
| Benzo[a]pyrene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Benzo[e]pyrene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Benzo[a]anthracene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Chrysene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Benzo[b]fluoranthene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Benzo[j]fluoranthene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Benzo[k]fluoranthene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Dibenzo[a,h]anthracene | < 0.5 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | < 1.0 |
| Sum 24 PAHs | < 5.0 | < 10.0 | < 10.0 | < 10.0 |





